<script type ="module" >
let canvas = document .querySelector ("canvas" )
canvas.editContext = new EditContext ()
canvas.focus ();
</script >
<canvas > </canvas >
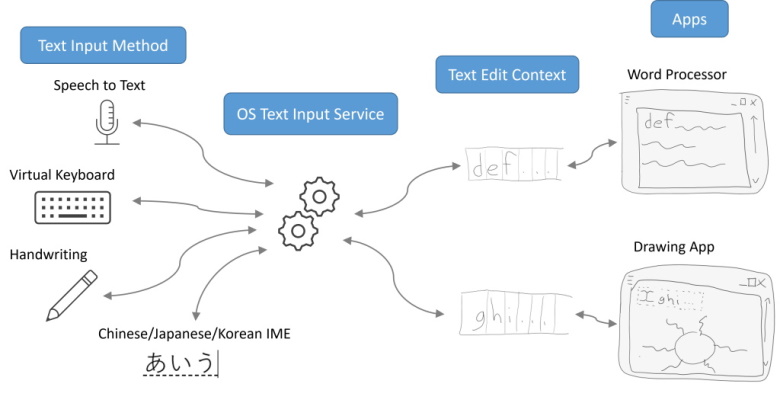
在下面的示例中,作者使用 canvas 来绘制一个可编辑区域,使用户可以输入使用等宽字体渲染的单行文本。该可编辑区域的文本由作者以 String 的形式维护;选区在可编辑区域中的文本偏移由作者以一对
Number(selectionStart 和 selectionEnd)维护,这两个 Number 表示从文本起始处到选区起点和终点分别包含多少个 UTF-16
码点。为了便于将当前选区和可编辑区域的边界矩形(使用 CSS 像素)告知文本输入服务,作者还会计算选区及可编辑区域在文档中的边界矩形。这些矩形的偏移相对于 canvas 元素的原点给出,因为作者正是将
EditContext associated
到该 canvas 元素上的。由于作者对文本和选区位置的表示方式与 EditContext API 期望的形式一致,作者只需在这些值变化时,将它们赋值给与 canvas associated 的 EditContext 即可。
<script type ="module" >
class EditingModel {
constructor (text, selectionStart, selectionEnd ) {
this .text = text
this .selectionStart = selectionStart
this .selectionEnd = selectionEnd
}
}
class EditingView {
constructor (canvas, model ) {
this .canvas = canvas
this .model = model
}
render (let canvasContext2D = this .canvas .getContext ("2d" );
canvasContext2D.strokeText (this .model .text );
}
computeSelectionBound (computeControlBound (class EditingController {
constructor (model, view, editContext ) {
this .view = view
this .model = model
this .editContext = editContext
}
render (render ()
let editContext = this .canvas .editContext
this .editContext .updateText (0 , this .model .text .length , this .model .text )
this .editContext .updateSelection (this .model .selectionStart , this .model .selectionEnd )
let selectionBounds = view.computeSelectionBound ()
let controlBounds = view.computeControlBound ()
editContext.updateSelectionBounds (selectionBounds)
editContext.updateControlBounds (controlBounds)
}
}
let canvas = document .querySelector ("canvas" )
canvas.editContext = new EditContext ()
let editingModel = new EditingModel ("" , 0 , 0 , 0 , 0 )
let editingView = new EditingView (canvas, editingModel)
let editingController = new EditingController (editingModel,
editingView, canvas.editContext );
editingController.render ()
</script >
<canvas > </canvas >
Example
3 :TextUpdateEvent、TextFormatUpdateEvent 与
CharacterBoundsUpdateEvent 的事件处理程序
<script >
class EditingModel {
updateText (updateRangeStart, updateRangeEnd, updateText ) {
this .text = this .text .substring (0 , updateRangeStart) + updateText
+ this .text .substring (updateRangeEnd)
}
updateSelection (selectionStart, selectionEnd ) {
this .selectionStart = selectionStart
this .selectionEnd = selectionEnd
}
updateTextFormats (textFormats ) {
this .textFormats = textFormats
}
}
class EditingView {
render (this .model .textFormats .forEach ( textFormat =>let lineStartX = anchorX + textFormat.rangeStart * charWidth;
let lineEndX = anchorX + textFormat.rangeEnd * charWidth;
canvasContext2D.lineWidth = (textFormat.underlineThickness == 'Thick' )?
thickWidth : thinWidth;
canvasContext2D.beginPath ();
canvasContext2D.moveTo (lineStartX, lineY);
canvasContext2D.lineTo (lineEndX, lineY);
canvasContext2D.stroke ();
})
}
computeCharacterBounds (rangeStart, rangeEnd ) {
}
}
class EditingController {
handleTextUpdate (updateRangeStart, updateRangeEnd, text,
selectionStart, selectionEnd ) {
this .model .updateText (updateRangeStart, updateRangeEnd, text)
this .model .updateSelection (selectionStart, selectionEnd)
}
handleTextFormatUpdate (textFormats ) {
this .model .updateTextFormats (textFormats);
}
handleCharacterBoundsUpdate (rangeStart, rangeEnd ) {
characterBounds = this .view .computeCharacterBounds (rangeStart, rangeEnd);
this .editContext .updateCharacterBounds (rangeStart, characterBounds);
}
}
editContext.addEventListener ("textupdate" , e =>handleTextUpdate (e.updateRangeStart , e.updateRangeEnd , e.text ,
e.selectionStart , e.selectionEnd )
});
editContext.addEventListener ("textformatupdate" , e =>handleTextFormatUpdate (e.getTextFormats ());
});
editContext.addEventListener ("characterboundsupdate" , e =>handleCharacterBoundsUpdate (e.rangeStart , e.rangeEnd );
});
</script >